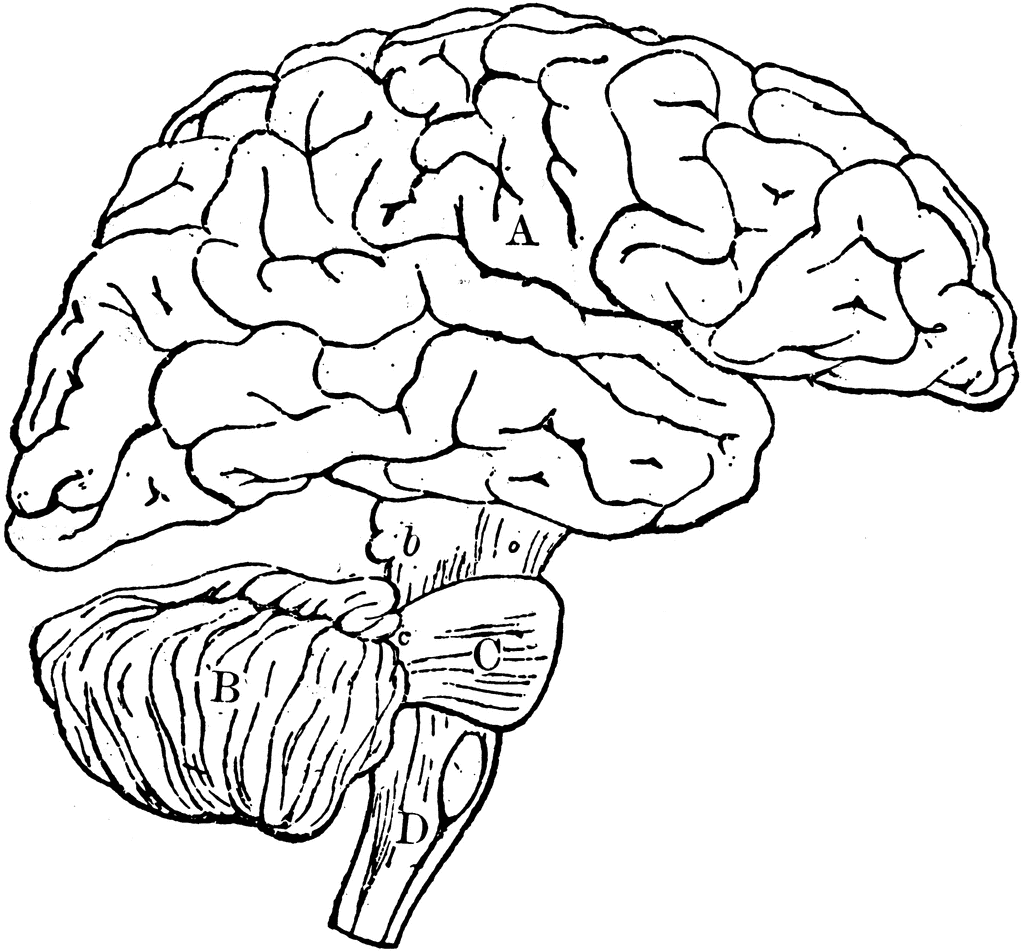
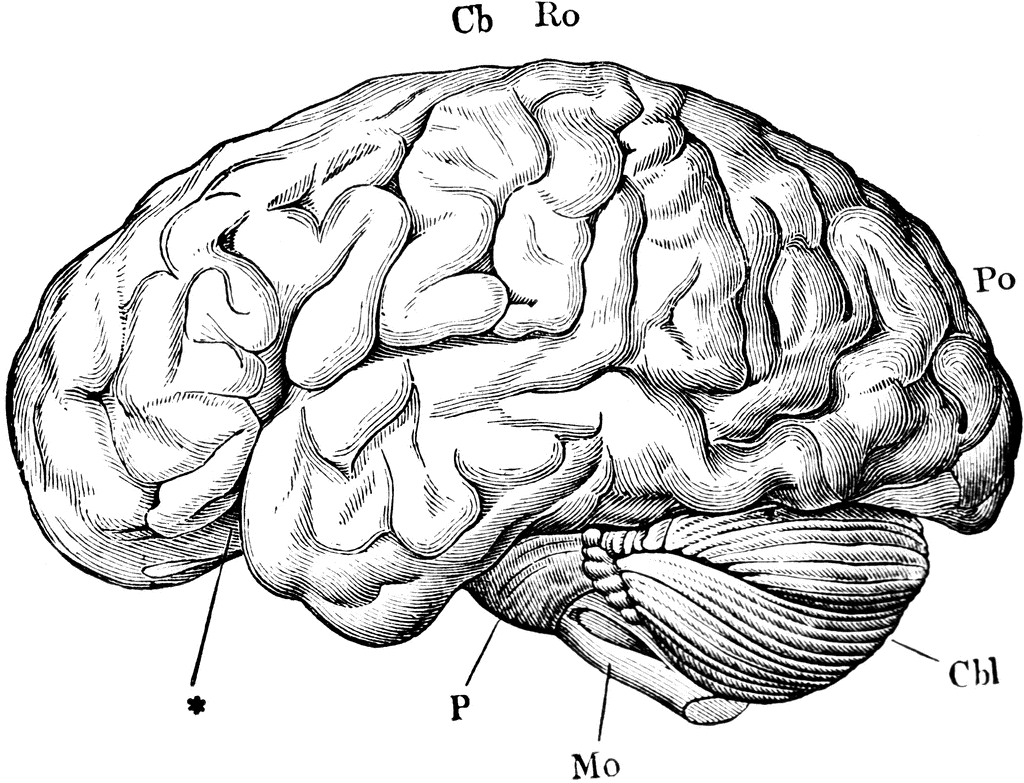
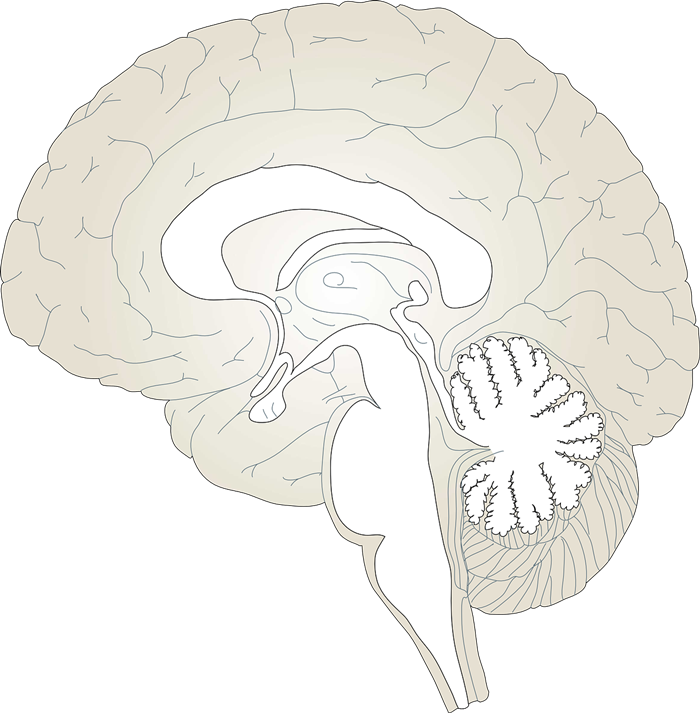
Brain Clip Art
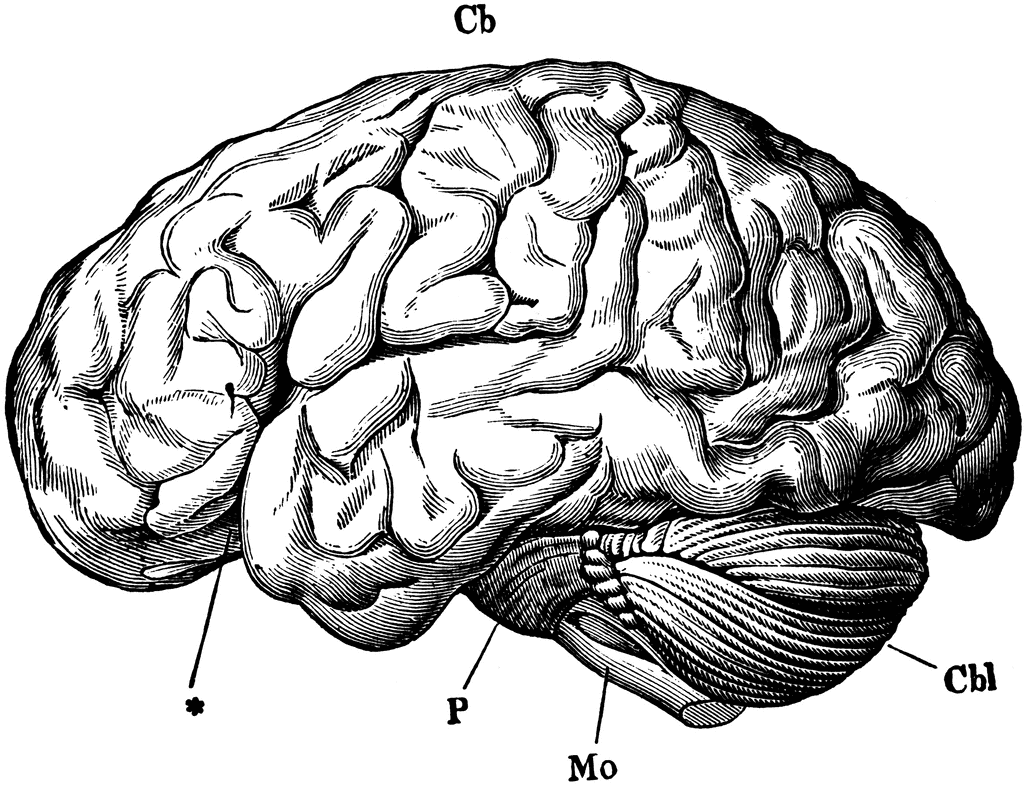
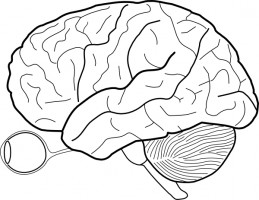
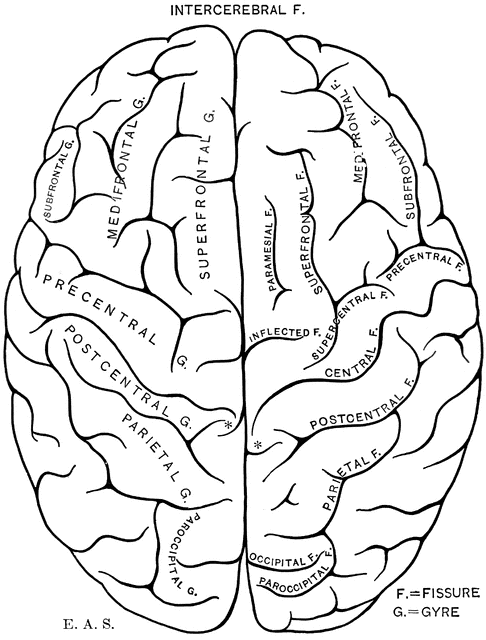
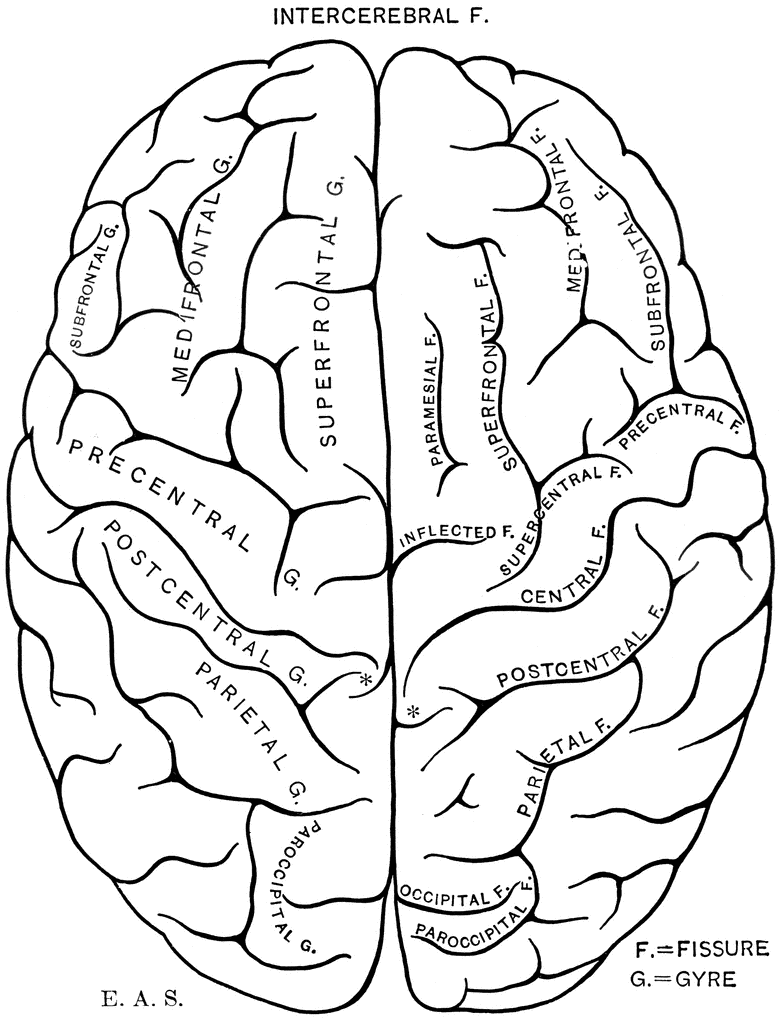
The brain is one of the most complex organs in the human body. It is made up of over 100 billion neurons and divided into several major regions. The largest region is the cerebrum, which controls cognition, sensory perception, emotion, consciousness, and muscle control. The cerebellum controls coordination and balance, while the brain stem controls critical functions like breathing and heart rate.
Functions of the Brain
The many functions of the brain can be broadly grouped into 3 categories: processing and integrating information from our senses, controlling bodily functions, and cognition and emotions. The brain collects information about our environment and our internal physiological states in order to create a cohesive representation of our experience. It controls basic functions like heart rate, breathing, waking and sleeping on a subconscious level. And on a conscious level, it performs higher order functions like storing memories, learning new information, controlling behavior, and creating our personality. Understanding these key functions provides insight into how the brain influences our fundamental human experience.
Brain Imaging Techniques
Brain imaging techniques like MRI, CT scans, and PET scans allow researchers and medical professionals to non-invasively peer into the structure and functioning of the living brain. MRIs provide detailed anatomical maps of brain structure and anatomy. CT scans reveal bone lesions, hemorrhages, and some tumors. PET scans show metabolic processes within the brain at the cellular level. Together these techniques are providing unprecedented visualization of brain functioning in health and disease.
Major Brain Disorders
Dementia, stroke, brain tumors, and traumatic brain injury are among some of the major disorders that affect the brain. Dementia is a category of progressive degenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s that cause impairments in memory, behavior and cognition. A stroke occurs when an artery bringing oxygen and nutrients to the brain is blocked, damaging brain tissue. Brain tumors cause disruption by compressing and invading healthy brain tissue. And trauma from repeated concussions to more catastrophic injuries can have short and long term impacts on brain functioning. Developing treatments for these and other disorders is a major priority for neuroscience.
History of Brain Science
Our understanding of the human brain has evolved over millennia, from prescientific notions of the purpose of brain tissue, to phrenology’s flawed attempt to link skull anatomy with specific mental aptitudes. With the advent of modern neuroscience in the 20th century, researchers developed more sophisticated theories of brain functioning, unlocking mysteries like the role of neurotransmitters in brain signaling and making formative links between brain physiology and complex cognitive phenomena, though much still remains unknown.
Famous Brains
The brains of famous people like Albert Einstein, Walt Whitman, and Carl Gauss have been extensively studied over time. Examination of Einstein’s brain after his death revealed unusual anatomical proportions which scientists speculated could be linked to his intellectual gifts, though no definitive conclusions could be drawn. Other famous brains demonstrate normal proportions, indicating that cognitive exceptionality arises from microscopic cellular configurations, highlighting the complexity of brain-behavior connections.
Brain Facts and Statistics
Though the human brain weighs just 3 pounds on average, it contains about 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion synaptic connections. Electrical signals in your brain travel as fast as 268 miles per hour. Despite its massive interconnectedness, sections of brain circuitry remain highly specialized – the fusiform face area plays a key role facial recognition, while Broca’s area drives speech production. Loss of brain tissue does not directly correlate with cognitive decline – Einstein’s brain weighed considerably less than average. These and many more facts illustrate the complexity and wonder of the human brain.
Brain Metaphors
We have devised numerous metaphors related to our enigmatic brains, from encouraging colleagues to “brainstorm” new ideas, to complaining about something being “brainless.” We talk about “having something on the brain” when preoccupied with particular thoughts. And memorizing something “by heart” equates retaining key knowledge as intrinsic as an organ critical for life. These turns of phrase underscore the essential nature of our brains to our human identity.
Brain Clipart and Illustrations
Clip art depicting the brain through schematic diagrams, cartoon illustrations, and detailed naturalistic renders serve an important function in allowing us to quickly communicate key information nonverbally. Colorful brain graphics distill concepts ranging from child brain development, to the specialized regions of the limbic system, to the anatomical deviations that underpin disorders like autism and schizophrenia. They illuminate complex physiology in easily accessible visual metaphors.
The Future of Neuroscience
Our comprehension of the brain has accelerated tremendously, but still comprises only rudimentary insights into its inner workings. Future advances in imaging technology and growth in interdisciplinary collaborations promise an ever more profound grasp of the biological basis of cognition, memory, emotion, consciousness and more. Banishing brain diseases remains a top priority, while aspirations like directly interfacing brains with computers via neural lace suggest a cyborgian direction for human evolution. Wherever new frontiers emerge, our curiosity about this mysterious organ undoubtedly persists.
In this page clipartix present 44 brain clipart images free for designing activities. Lets download Brain Clip Art that you want to use for works or personal uses.