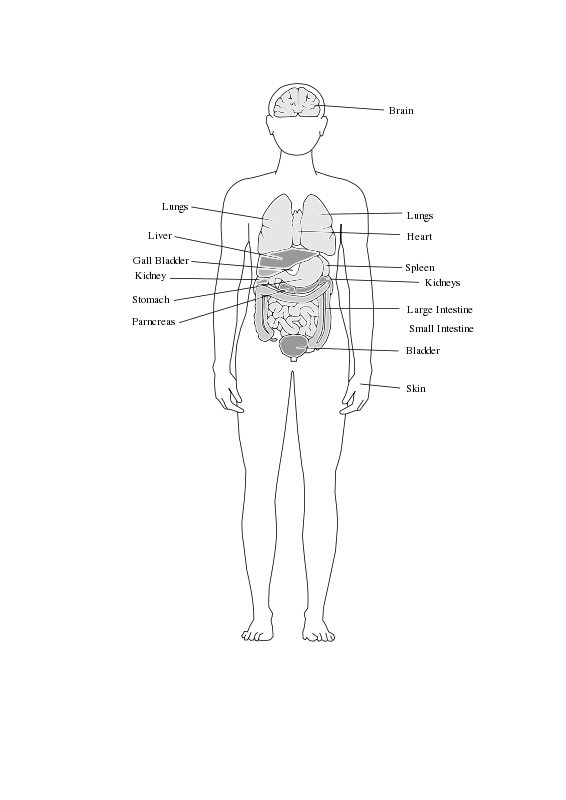
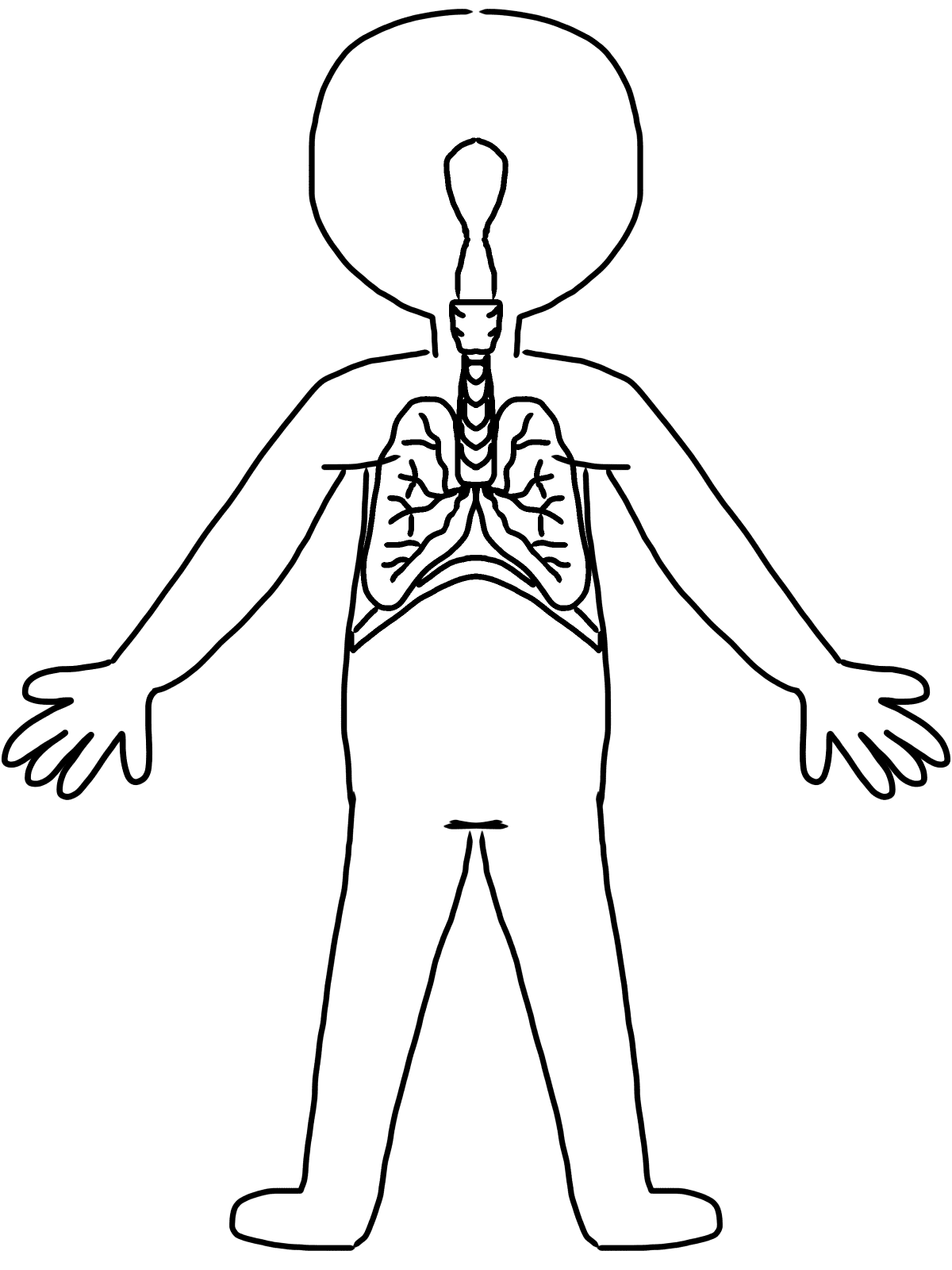
Body Clipart
The human body is an incredibly complex machine. It is made up of over 200 bones, 650 muscles, and countless cells that all work together to sustain life. Multiple systems carry out specific bodily functions, with each system relying on the others to maintain normal operation. This article will provide an overview of the body’s major systems and discuss how anatomical clipart can help illustrate the body’s intricacies.
Major Systems of the Body
The body contains 11 major organ systems that work in tandem to keep us alive. These include:
- Circulatory system – transports blood throughout the body via the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries
- Digestive system – breaks down food and absorbs nutrients for energy
- Endocrine system – produces hormones that regulate bodily functions
- Immune system – protects the body from illness and infection
- Integumentary system – includes hair, skin, nails and sweat glands
- Muscular system – enables body movement through skeletal muscles
- Nervous system – collects and processes information via the brain, nerves and sensory organs
- Reproductive system – produces sex cells and hormones for reproduction
- Respiratory system – brings air into and out of the lungs for gas exchange
- Skeletal system – provides support, protection and frame for the body
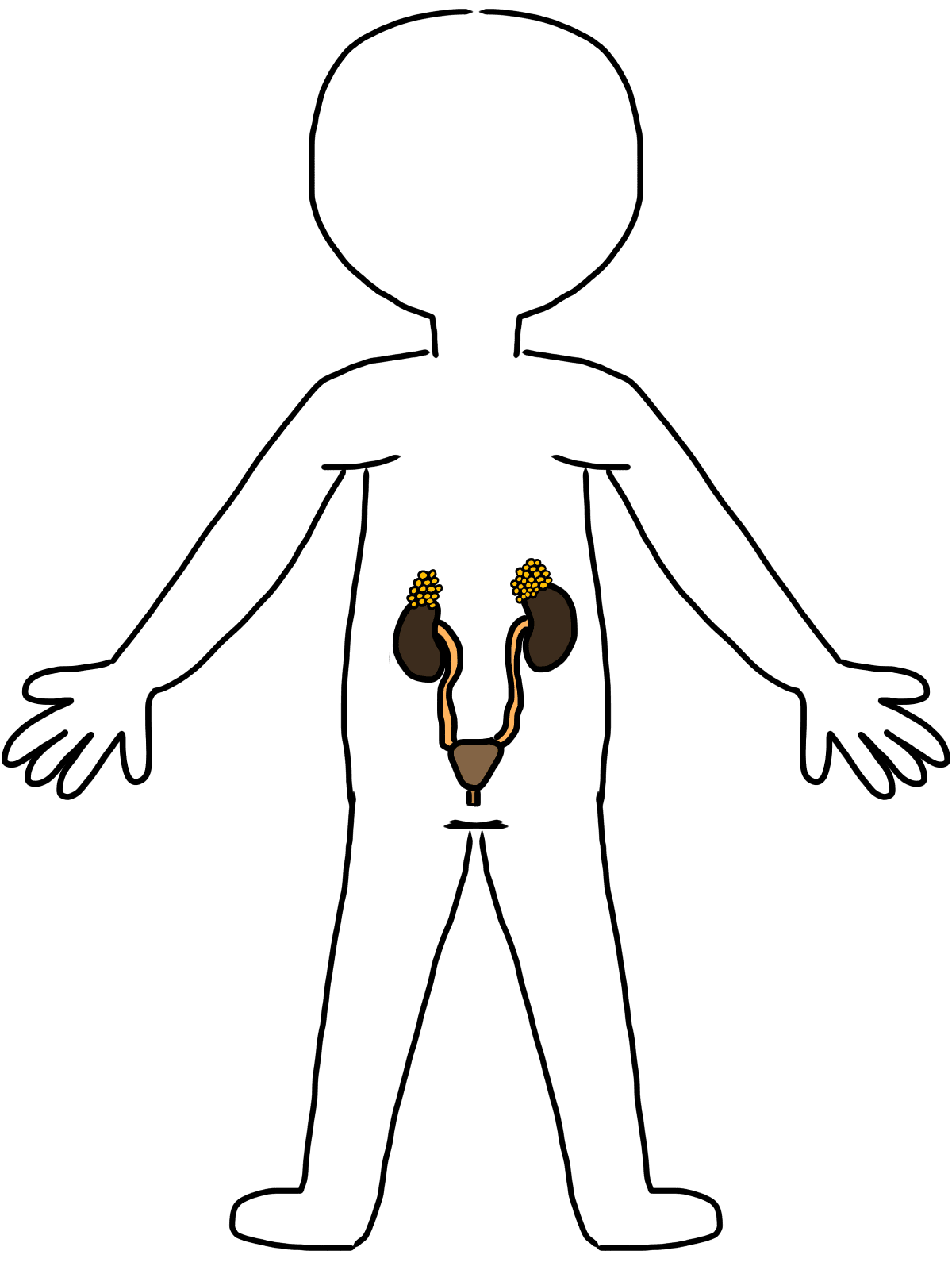
- Urinary system – removes liquid waste from the body
Bones and the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is composed of 206 bones that provide structure and protection for the body. Key functions include:
- Support – the skeletal frame supports softer body tissue
- Protection – bones protect internal organs from external damage
- Movement – skeletal muscles attach to bones, enabling body motions
- Storage – bone marrow produces blood cells, and bones store minerals
There are several types of bones, including long bones in the arms and legs, short bones in the wrists and ankles, flat bones like the skull and shoulder blades, irregular bones with complex shapes, and sesamoid bones within tendons. Bone composition is almost 70% minerals like calcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite crystals, allowing for bone hardness.
Muscles and the Muscular System
There are over 650 skeletal muscles in the body divided into three types:
- Smooth muscle – found in organs and blood vessels, stretch involuntary to move substances through organs
- Cardiac muscle – forms the heart wall to enable involuntary pumping
- Skeletal muscle – connects to bones by tendons to produce voluntary body movements like walking
Major skeletal muscles include the gluteal muscles in the buttocks that support body weight, abdominal muscles that flex and rotate the trunk, and the quadriceps in the thighs that straighten the leg. When a muscle contracts through signals carried by neurons, the fibers shorten to generate force and motion.
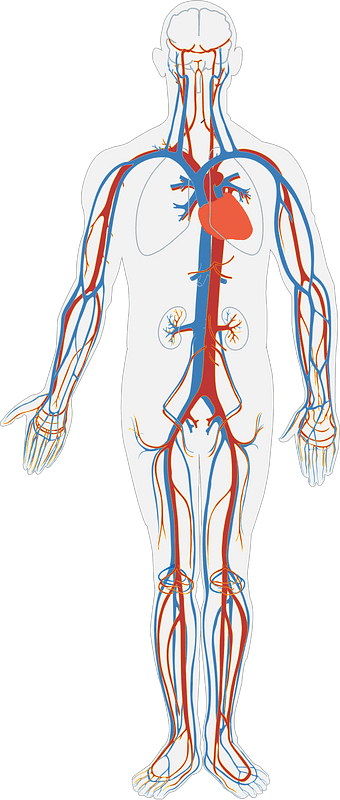
The Heart and Circulatory System
The circulatory system transports essential substances throughout the body. This is accomplished through blood pumped by the heart, arteries distributing blood, veins returning blood to the heart, and capillaries exchanging substances with cells.
The heart contains four chambers encased in a sac called the pericardium – two upper atria and two lower ventricles. The cardiac cycle consists of two phases:
- Diastole: the ventricles relax as they fill with blood
- Systole: ventricular muscles contract to pump blood into arteries
One-way valves prevent back flow as blood circulates from the heart to lungs to exchange gases, then back to the heart to be pumped throughout the body.
Lungs and the Respiratory System
The key organs of the respiratory system function to bring oxygen into the body and expel carbon dioxide in a gas exchange process known as breathing. Air first enters the nose and mouth, passing the pharynx and larynx on the way to the trachea. The trachea splits into smaller bronchi that enter left and right lungs filled with bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli air sacs.
Inhalation occurs when the diaphragm muscle contracts downward, increasing chest cavity volume and lowering air pressure to suck air into the lungs. Exhalation results from diaphragm relaxation pushing air back out of the lungs. Gas exchange with blood occurs in the alveoli through diffusion.
The Nervous System and Brain Function
The nervous system has a vital role collecting sensory information, processing it, and initiating responses. Special sensory neurons detect stimuli like light, sound, touch, pain, position, etc. This signal travels to the spinal cord to convey messages to and from the brain rapidly.
The brain is the master command center made up of many specialized regions and nuclei:
- Cerebrum – involved in conscious thought, reasoning, movement
- Cerebellum – coordinates voluntary motions
- Brain stem – regulates involuntary actions like breathing and circulation
- Hypothalamus – releases hormones and controls temperature regulation
Complex networks of billions of interconnected nerve cells or neurons enable lightning quick communication.
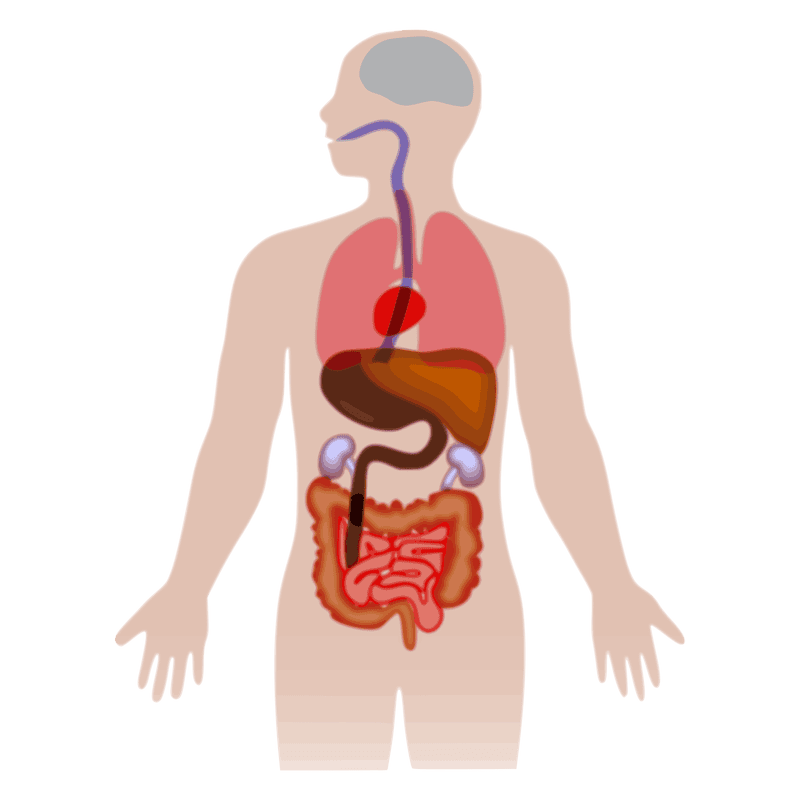
The Digestive System and Organs
Digestion involves breaking food down into molecules small enough for absorption and processing by the body. It begins in the mouth, followed by three sections of the gastrointestinal tract specialized for digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Oral cavity – mechanical digestion by chewing and chemical breakdown by salivary enzymes
- Pharynx and esophagus – pushes food towards stomach through wave-like muscular contractions called peristalsis
- Stomach – secretes acids, digestive enzymes, and hormones; small intestine continues chemical digestion
Accessory organs like the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder produce secretions that facilitate digestion. The lining of the small intestine absorbs digested sugars, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and electrolytes into the bloodstream.
The Reproductive System and Organs
The reproductive system allows humans to produce children. It contains internal and external reproductive organs with key differences between males and females.
Male Reproductive Anatomy
- Testes – produce sperm and hormones like testosterone
- Epididymis – stores and matures sperm
- Vas deferens – carry sperm towards urethra
- Ejaculatory ducts – add secretions to form semen
- Urethra – transports both urine and semen
- Penis – delivers semen into the female vagina during intercourse
Female Reproductive Anatomy
- Ovaries – generate ova or egg cells and estrogen/progesterone hormones
- Uterus – supports development of a fetus during pregnancy
- Cervix – lower portion of the uterus opening into the vagina
- Fallopian tubes – carry eggs from ovaries to uterus
- Vagina – muscular canal terminating at the vulva and cervix
Body Clipart to Illustrate Anatomy
Anatomical clipart can enhance comprehension of bodily structures through detailed artistic diagrams. Images clearly outline individual muscles, organs, arteries, veins, nerves, and skeletal structure. Visual learners benefit from matching clipart pictures to vocab terms when memorizing parts of organ systems.
Clipart sets are available showing just the circulatory system, digestive tract, regions of the brain, reproductive organs, cells, embryos, and more. File formats like PNG work well inserted into study guides, presentations, infographics, and medical reports when detailed anatomy illustrations are needed. Some sets even depict biomechanical functions like tendons contracting and the heart beating.
In conclusion, the intricate coordination between body systems, tissues and cells keeps us all alive. Anatomical clipart has great value enhancing our understanding of this amazing living machine we inhabit!
In this page clipartix present 57 body clipart images free for designing activities. Lets download Body Clipart that you want to use for works or personal uses.